Due to the polar vortex’s substantial impact on global weather patterns, particularly in North America and Europe, it has become a well-known meteorological phenomenon in recent years. Although this natural phenomenon is not a novel idea in the world of meteorology, it has gained increasing attention in the media. We shall go into great detail about the polar vortex in this essay, including its properties, causes, and impacts.
Understanding the Polar Vortex
What is the Polar Vortex?
A significant, long-lasting low-pressure system known as the polar vortex frequently dwells over the polar regions, especially in the Arctic during the winter. High in the Earth’s atmosphere, it is a swirling mass of extremely cold air that is focused around the North and South Poles.
Structure of the Polar Vortex:
The tropospheric polar vortex and the stratospheric polar vortex are the two main parts of this phenomena. The tropospheric vortex is located closer to the Earth’s surface in the lower levels of the atmosphere, whereas the stratospheric vortex is found in the highest layers.
Causes and Mechanism of Polar vortex
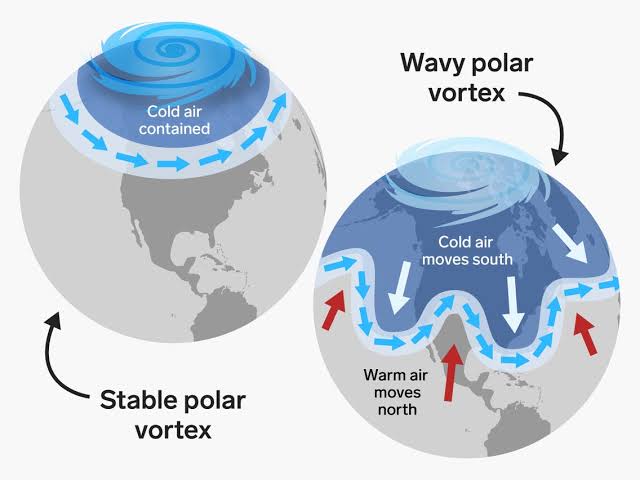
Cold Air Trapped:
When there is a significant temperature difference between the polar regions and the mid-latitudes, the polar vortex forms. Extreme cold in the Arctic throughout the winter creates a stark temperature difference between the poles and areas further south.
Jet Streams:
The jet streams, which are swift-moving, slender air currents in the high atmosphere, have an impact on the polar vortex. The stability and mobility of the vortex may be impacted by the interaction between the polar jet stream and the subtropical jet stream.
Stratospheric Warming Events:
The polar vortex can occasionally be broken up by stratospheric disturbances like sudden stratospheric warming events. These occurrences may cause the vortex to weaken or split, allowing cold air to enter lower latitudes.
Effects of the Polar Vortex
Extreme Cold:
The polar vortex’s chilling, sub-zero temperatures it brings to areas close to and distant from the poles are its most noticeable immediate effect. Frostbite, extreme cold spells, and even infrastructure problems like frozen pipes can come from this.
Snowfall and Storms:
It can cause weather patterns to change as the polar vortex weakens or meanders, which can boost snowfall and winter storm activity in regions with generally warmer winters.
Disrupted Jet Streams:
The polar vortex’s behavior can influence the jet streams, which in turn affects weather patterns over large regions. This can result in prolonged periods of cold or unseasonably warm weather.
Impact on Agriculture:
Extreme cold from a polar vortex can harm crops and livestock, leading to agricultural losses.
Conclusion
Winter weather patterns are significantly influenced by the polar vortex, a natural meteorological phenomena, particularly in the Northern Hemisphere. The understanding of its causes and effects enables meteorologists to better predict and prepare for its affects, even if it may bring extreme cold and difficult conditions. The study of the polar vortex is a crucial component of meteorological research and forecasting as the world’s climatic patterns continue to change, enabling us to adapt to and lessen its effects.
FAQs
What is the polar vortex?
The polar vortex is a large area of low pressure and cold air surrounding both of the Earth’s poles.
What is the polar vortex for UPSC?
What is a Polar Vortex? A polar vortex or polar low-pressure area is a vast region with low-strain and freezing air covering both the planet’s poles.
How is a polar vortex formed?
Polar vortex is the name given to the strong currents of wind formed by low pressure that occurs in the Arctic and Antarctic regions. The name originates from the fact that these winds circulate and form a vortex near the North and South Poles of the planet.
Does polar vortex affect India?
Some research claims that there is no direct relation between the Polar Vortex and Indian weather but the Arctic winds are influence the various weather systems, including the western disturbance, downwards.
What is an example of a polar vortex?
For example, the 2013–14 United Kingdom winter floods were blamed on the Polar vortex bringing severe cold in the United States and Canada. Similarly, the severe cold in the United Kingdom in the winters of 2009/10 and 2010/11 were also blamed on the Polar vortex.
Which planet has a polar vortex?
Polar vortices seem to be a common trait of all planets with atmospheres, at least in our solar system – they have been previously observed on Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus (at its south pole) and Neptune.
Is there a polar vortex in the US?
Many times during winter in the northern hemisphere, the polar vortex will expand, sending cold air southward with the jet stream (see graphic above). This occurs fairly regularly during wintertime and is often associated with large outbreaks of Arctic air in the United States.


